Category Science & Technology
Programming cells to organize their molecules may open the door to new treatments
Biochemists at UW–Madison have developed a tool to control how certain proteins move in mammalian cells, a discovery that has multiple potential uses for treating or studying diseases by engineering specific cellular activities or studying cellular activity in a living organism. Read More
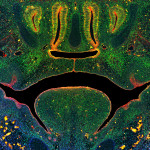
UW–Madison researchers first to 3D-print functional human brain tissue
It’s an achievement with important implications for scientists studying the brain and working on treatments for a broad range of neurological and neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Read More
These tomatoes are out of this world… or they will be soon
By sending tomato plants to the International Space Station, UW researchers hope to better understand how plants grow without gravity and whether there are ways to help plants cope with the stressors involved with growing in space flight. Read More
Chats with AI shift attitudes on climate change, Black Lives Matter
Researchers studying AI wanted to understand how one complex large language model, GPT-3, would perform across a culturally diverse group of users in complex discussions. Read More
How ’bout that weather we’re having? A Q&A with Wisconsin’s State Climatologist.
This year, the onset of cold temperatures, substantial snowfall and ice over on some Wisconsin's most iconic lakes happened later than usual. Why? Read More
National committee co-chaired by Chancellor Mnookin issues report on facial recognition technology
Chancellor Jennifer L. Mnookin co-chaired a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine committee that issued a report recommending the federal government take action to address privacy, equity and civil liberties concerns in light of facial recognition technology that has outpaced laws and regulations. Read More
Earth-sized planet discovered in ‘our solar backyard’
A team of astronomers have discovered a planet closer and younger than any other Earth-sized world yet identified. It’s a remarkably hot world whose proximity to our own planet and to a star like our sun mark it as a unique opportunity to study how planets evolve. Read More
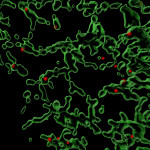
UW–Madison scientists reveal the inner workings of an essential protein trafficking complex
The discovery could eventually help researchers better understand and develop new treatments for diseases like cancer, diabetes and those that cause immune dysfunction. Read More
Multitasking microbes: UW–Madison scientists engineer bacteria to make two valuable products from plant fiber
UW researchers have engineered bacteria that can produce two chemical products at the same time from underutilized plant fiber. The discovery could help make biofuels more sustainable and commercially viable. Read More
Stem cell technology developed at UW–Madison leads to new understanding of autism risks
Ashton says researchers using technologies like the RosetteArray are finding that the risk factors for autism spectrum disorder are boiling down to a couple of core pathways, that seem to have roles very early in human brain development, which is helpful information as researchers work on treatments. Read More
Mineral coatings could enable shelf-stable mRNA therapies
A protective mineral coating identified by University of Wisconsin–Madison biomedical engineering researchers could allow powerful messenger RNA therapeutics like COVID-19 vaccines to be stored at room temperature, making them more accessible to lower-resourced communities across the world. Read More
Newly developed material gulps down hydrogen, spits it out, protects fusion reactor walls
The advance, detailed in a paper published recently in the journal Physica Scripta, could enable more efficient compact fusion reactors that are easier to repair and maintain. Read More
Zapping manure with special electrode promises an efficient method to produce fertilizers, other chemicals
The researchers' preliminary analyses show it could offer considerable benefits by cutting water and air pollution while simultaneously creating products that farmers could use or sell. Read More
Federal physics advisory panel recommends funding next generation IceCube observatory, other major experiments
A group of scientists tasked with advising the federal government's investments in particle physics research is recommending that the United States fund a planned expansion of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, an international scientific collaboration operated by the University of Wisconsin–Madison at the South Pole. Read More
Prohibition may have extended life for those born in dry counties
Using advanced analytical methods on data from the Prohibition Era, research findings provide important nuance to the assessment of Prohibition’s effects on public health and could have important implications for policies aimed at reducing maternal alcohol use. Read More
UW–Madison remains 8th in research ranking, surpasses $1.5 billion in research expenditures
The NSF today released its Higher Education Research and Development (HERD) data showing a 10% increase in research expenditures at UW–Madison over the previous fiscal year, or more than $143 million for the period covering July 2021 and the end of June 2022. Read More